Natural gas supply and demand grew at their fastest pace since 2010
 According to CEDIGAZ report “The Global Gas Market – 2019 Edition”, 2018 has been a remarkable year for the global natural gas market.
According to CEDIGAZ report “The Global Gas Market – 2019 Edition”, 2018 has been a remarkable year for the global natural gas market.
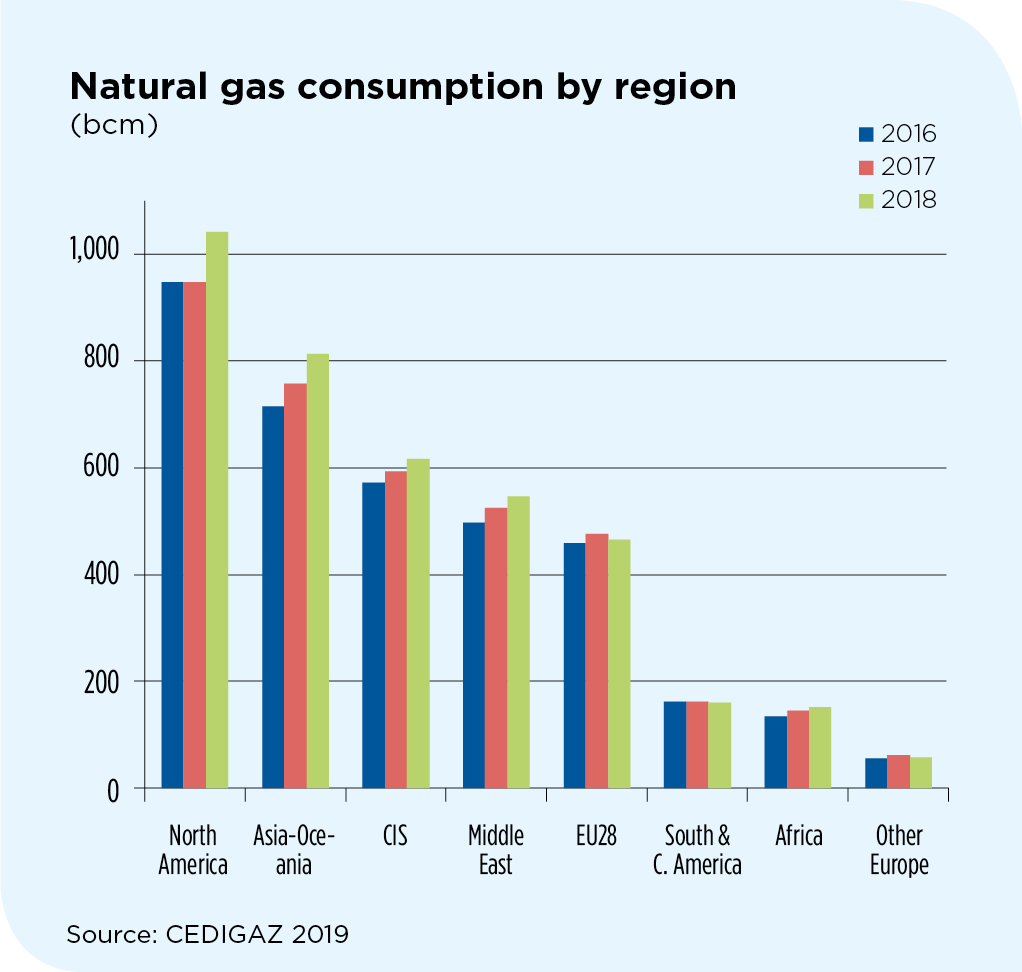
Global natural gas demand surged 4.7% to 3850 bcm, driven by the US and China. The US was the standout performer, accounting for 45% of the global increase in both the consumption and supply of natural gas.
2018 marks the second year of strong growth of natural gas demand, after a 3.5 % rise in 2017. It also recorded the highest growth of gas demand since the post-crisis rebound of 2010.
This fast expansion was driven by the abundance of competitive gas supply, especially in the US and in Russia and by supportive energy and environmental policies, in some countries, particularly in China. Investment in transport infrastructure also contributed to bolster gas penetration in key markets.
China became the largest net importer of natural gas in the world before Japan. Chinese net imports jumped by 32% and accounted more than 80% of the global increase in net imports, once again highlighting the crucial role of China in absorbing global gas production.
Like in 2017, the expansion of natural gas demand was part of a substantial global growth in world energy demand, driven by a robust global economy and extreme weather conditions.
Strong gas demand growth in Asia contributed to a rise in market prices in key areas and prevented the formation of a global LNG bubble.